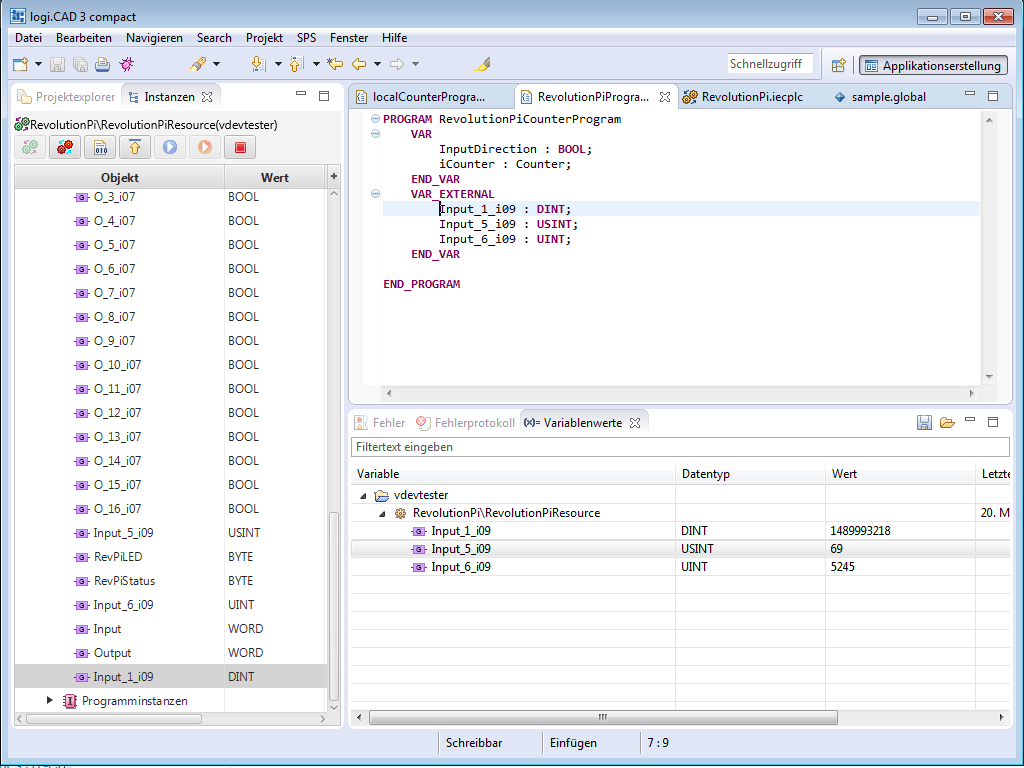
We use RevPiModIODriver() to develop a driver for a virtual device in piCtory.
In our example, we collect data from the RevolutionPi and write it into a virtual device. This is the system time in UTC, the percentage of disk space, and the CPU temperature.
These data are then available to programs such as logiCAD.# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import revpimodio2
import time
from os import statvfs
class MyDriver():
def __init__(self):
"""Instantiates the driver."""
# Instantiate RevPiModIODriver for virtual device on position 64
self.rpi = revpimodio2.RevPiModIODriver(64, autorefresh=True)
# Handle exit signal from operating system or Ctrl+C Signal to exit
# the driver cleanly
self.rpi.handlesignalend()
# RevPiModIODriver: Configure inputs to write data
# We are the DRIVER an CAN write into INPUTS!!!
# Use Input-Byte 0 to 3 as int for timestamp
self.rpi.io.Input_1.replace_io("timestamp", "L")
# Input byte 4 as int use for n% allocation root mount
self.rpi.io.Input_5.replace_io("roothdused", "B")
# Input-Byte 5 - 6 as int for CPU temperature * 100 (centi degree)
self.rpi.io.Input_6.replace_io("cputemp", "H")
def cyclefunction(self, cycletools):
"""This function is called cyclically by RevPiModIODriver."""
# Timestamp - Write RevPi-Time
self.rpi.io.timestamp.value = int(time.time())
# Storage of the root mount
hd = statvfs("/")
usedspace = int(
(hd.f_blocks - hd.f_bavail) / hd.f_blocks * 100
)
self.rpi.io.roothdused.value = usedspace
# CPU-Temperature
with open("/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp") as fh:
tmp = fh.read()
self.rpi.io.cputemp.value = int(tmp.strip()[:-1])
def start(self):
"""Start the cycleloop to execute the 'cyclefunction' cyclically."""
# The program blocks at this point an runs the loop. We set the cycletime
# to 1000 milliseconds - thats enough for refresh the data.
self.rpi.cycleloop(self.cyclefunction, cycletime=1000)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = MyDriver()
root.start()
import revpimodio
import signal
import time
from os import statvfs
from threading import Event
class MyDriver():
def __init__(self):
"""Instantiates the driver."""
self._evt_exit = Event()
# Load configuration
self._loadconfig()
# Signal events
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, self._sigexit)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, self._sigexit)
signal.signal(signal.SIGHUP, self._loadconfig)
def _loadconfig(self, signum=None, frame=None):
"""Load/Reload configuration."""
# Instantiate RevPiModIODriver
self.rpi = revpimodio.RevPiModIODriver([64])
# Configure RevPiModIODriver
# Use Input-Byte 0 to 3 as int for timestamp
self.rpi.devices[64].reg_out("timestamp", "Input_1_i09", "L")
# Input byte 4 as int use for n% allocation root mount
self.rpi.devices[64].reg_out("roothdused", "Input_5_i09", "B")
# Input-Byte 5 - 6 as int for CPU temperature * 100 (centi degree)
self.rpi.devices[64].reg_out("cputemp", "Input_6_i09", "H")
# After run() pass These seconds wait until re-run
self.refresh = 1
def _sigexit(self, signum, frame):
"""Signal handler to exit."""
self._evt_exit.set()
def run(self):
"""Runs until Exit is set."""
while not self._evt_exit.is_set():
# Inputs read, from the point of view of logiCAD these are outputs!
# (even if we're not using them at this moment)
self.rpi.devices.readprocimg()
# Timestamp - Write RevPi-Time
self.rpi.devices[64]["timestamp"].value = int(time.time())
# Storage of the root mount
hd = statvfs("/")
usedspace = int(
(hd.f_blocks - hd.f_bavail) / hd.f_blocks * 100
)
self.rpi.devices[64]["roothdused"].value = usedspace
# CPU-Temperature
with open("/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp") as fh:
tmp = fh.read()
self.rpi.devices[64]["cputemp"].value = int(tmp.strip()[:-1])
# Outputs from the point of view of logiCAD are inputs!
self.rpi.devices.writeprocimg()
# Wait
self._evt_exit.wait(self.refresh)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = MyDriver()
root.run()